1. Introduction
The basal ganglia level is an important horizontal section of the brain seen on CT and MRI.
It lies above the brainstem and below the centrum semiovale, at the level of the interventricular foramen (foramen of Monro).
It includes deep grey matter nuclei essential for motor control, behaviour, and cognition.
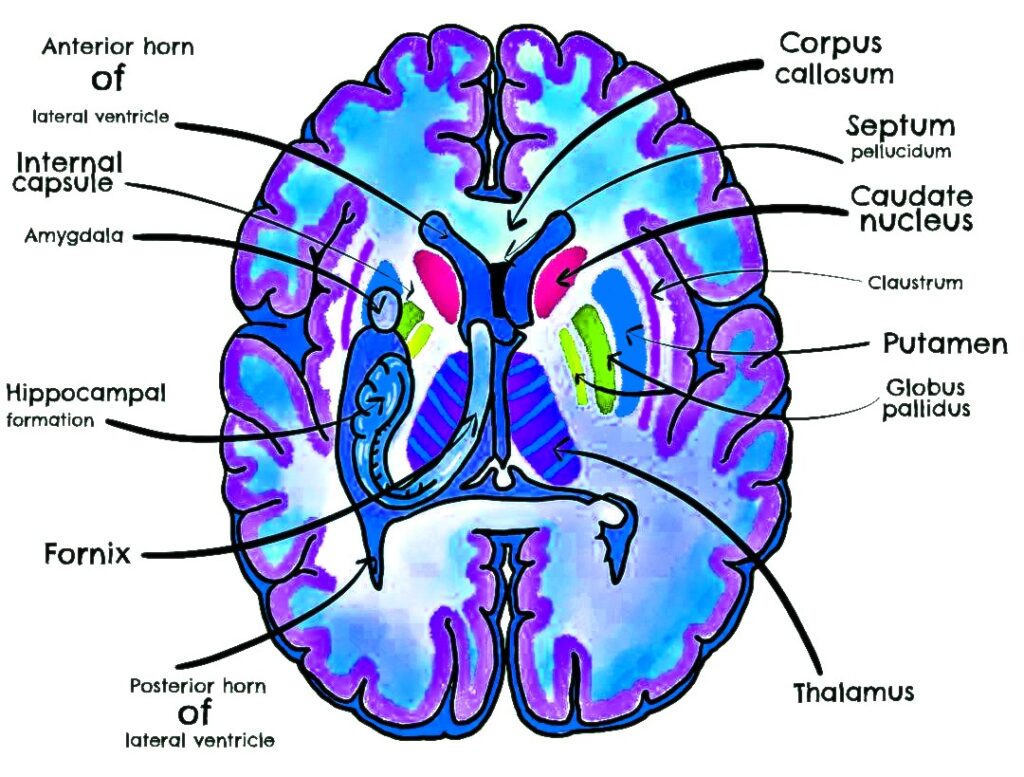
2. Major Structures Seen
A. Grey Matter Nuclei
- Caudate nucleus – head and body visible
- Lentiform nucleus – composed of:
- Putamen (lateral part)
- Globus pallidus (medial part, internal & external segments)
- Thalamus – medial to internal capsule posteriorly
- Claustrum – thin grey matter lateral to putamen
- Amygdala – anteromedial temporal lobe (seen in more inferior basal ganglia cuts)
B. White Matter Tracts
- Internal capsule – has three parts:
- Anterior limb (between head of caudate & lentiform nucleus)
- Genu (bend)
- Posterior limb (between thalamus & lentiform nucleus)
- External capsule – between putamen & claustrum
- Extreme capsule – between claustrum & insular cortex
- Corpus callosum – genu and body (superior to basal ganglia)
- Optic radiations (in posterior limb region)
C. Other Key Structures
- Insular cortex (lateral surface, deep to temporal and frontal opercula)
- Sylvian fissure with MCA branches
- Lateral ventricles – anterior horn and body
- Third ventricle – midline slit between thalami
- Basal forebrain structures – nucleus basalis of Meynert (in anterior-inferior slices)
3. Blood Supply
- Lenticulostriate arteries from middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- Anterior choroidal artery from ICA
- Recurrent artery of Heubner from ACA
4. Imaging Significance
- Stroke: Lacunar infarcts common in internal capsule, thalamus, or putamen
- Movement disorders: Parkinson’s (substantia nigra degeneration, indirect basal ganglia effects), Huntington’s (caudate atrophy)
- Wilson’s disease: Putaminal changes
- Metabolic disorders: Hypoxic-ischemic injury affects basal ganglia in children
- Infections: Japanese encephalitis often involves thalami and basal ganglia
5. Diagrammatic Representation
From medial to lateral (mnemonic: “Can I Get Perfect Exam In Summer?”)
- Caudate nucleus
- Internal capsule (anterior limb)
- Globus pallidus
- Putamen
- External capsule
- Insular cortex (via extreme capsule)
- Sylvian fissure
